Introduction
Are you worried about your devices when the current surges suddenly? Sometimes, the circuits catch fire and might injure you.
Luckily, you have the saviors here— the circuit breaker, which will interrupt current flow when needed. But there are too many circuit breakers in the market. Which one should you choose?
Today we will compare all types of device protectors for your home or commercial applications!
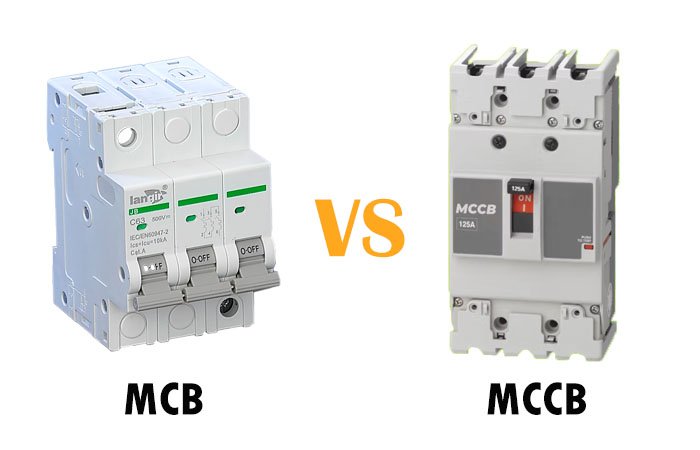
What Are MCB and MCCB?
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
MCB is a device that protects the appliances by breaking the current flow in the circuits in case of a surge. It is rated to handle the home wiring and is ideal for low-current circuits. MCB can handle a current range of 0.5A to 125A. Such circuit breakers are often part of home appliances and small setups, such as offline stores.

MCCB (Moulded Case Circuit Breaker)
Unlike the MCB, the MCCB is rated for medium to high current circuits. Therefore, such a device interrupts the flow of current in industrial settings while protecting the devices. It also provides temperature protection settings because of the bimetallic construction. It is suitable for high current ratings ranging from 100A to 2500A.
MCB vs MCCB
MCB and MCCB can have various things in common while differing at a few points.
Here are the same and different points between them.
Similarities
Protect appliances
MCB and MCCB have the same goal. Both interrupt the current supply to protect the devices from the surges.
Operation
The working mechanism is the same. They both cut off the current supply by breaking the circuit without manual intervention.
Safety
When operating these circuit breakers, there are no risks. Even they are the protectors.
Physical components
MCB and MCCB have almost the same components, with a switch and a trip mechanism to break the flow.
Appliances
The scope of applications varies, but both can be used for commercial and residential applications with a different current handling range.
Differences
Rated Current
MCB has a current rating maximum of up to 125A. Compared to it, there is a giant 2500A-rated current of MCCB.
Breaking Capacity
MCB has a breaking capacity of up to 10kA, while the MCCB is larger and has a capacity of 100kA.
Cost
MCB is a simple device with a cheaper price. At the same time, MCCB deployment is extensive and costly.
Size
MCB is small in structure with easy installation. On the other hand, MCCB can handle both thermal and electronic areas and has a large size.
Applications
The scope of the application is different. MCB is manufactured for small appliances and circuits, such as at home. At the same time, MCCB is helpful for large applications, especially in the commercial sectors.
The table highlights all the differences at once.
| Feature | MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) | MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) |
| Breaking Capacity | Up to 10 kA | Up to 100 kA |
| Rated Current Range | Up to 125 A | Up to 2500 A |
| Physical Size | Small and compact | Larger and bulkier |
| Tripping Curves | It has curves of B, C, D. | MCCB features extensive range of curves, such as A, B, C, D, K, Z. |
| Available Classes | MCB features B, C, D. | Extensive: A, B, C, D, K, Z, and more |
| Typical Application | Residential and small commercial loads | Industrial and large commercial systems |
| Cost | Economical | More expensive |
| Settings/Adjustability | Fixed trip settings | Adjustable (thermal & magnetic thresholds) |
| Overload Protection | Thermal (via bimetallic strip) | Thermal or electronic |
| Device Protection mechanisms | It is Magnetic (solenoid-based). | It can be either magnetic or electronic. |
| Disconnection Speed | Fast for lower fault levels | Adjustable delay for coordination |
| Reset Mechanism | Manual reset only | Manual or automatic reset |
What Is RCB, RCD, RCCB or RCBO?
RCB (Residual Current Breaker), or RCD (Residual Current Device), or RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker)
RCB, RCD and RCCB are not entirely different devices. Instead, they are a single device with a single goal to protect users from electrical shock.
Instead of detecting the surge in the circuits, this device cuts the current supply from the entire circuit when there is a leakage of current. The purpose is to maintain the same current flow in the line for the given time.
RCBO (Residual Circuit Breaker Over-current)
Let’s combine the functions of RCB and MCB. You get a residual circuit breaker overcurrent.
This device does both tasks— detects the current flow in the line and notices the surges. Whether there is a current leakage or high voltage surge, this device breaks the circuit and protects the appliances.
RCD vs. RCBO: Similarities and Differences
RCD and RCBO keep the users safe and share some common points. Here are similarities and differences.
Similarities
Earth leakage protection
Both types of circuit breakers offer a basic current leakage protection facility.
Improved electrical safety
Both devices prevent sudden electric shocks and are blessings for humans.
Quick response time
RCD and RCBO detect the current changes in milliseconds and respond instantly to cut off the circuit.
Installed in consumer units
You can install both in the electrical distribution unit or consumer unit.
The same principle of operation
RCD and RCBO use residual current sensing mechanisms and detect the current changes between live and neutral wires.
Differences
Type of protection
RCD offers only earth leakage protection, while RCBO provides additional features like short circuit safety and current overloading.
Circuit coverage
RCD can cover multiple circuits instead of individual security. At the same time, RCBO offers individual protection to each circuit with its advanced protection system.
Trip behavior
RCD cuts the supply to all the circuits, whether one circuit fails or multiple fails. On the other hand, RCBO blocks only the faulty circuit while current flows through the other circuit.
Space and wiring requirements
RCD can require the installation of MCB for circuit protection and needs extra space for more features. At the same time, the RCBO combines all the features simultaneously and saves additional space.
Cost and efficiency
RCD is cheaper but less efficient. In contrast, RCBO offers advanced features and high efficiency at a higher price.
Differences Between RCD and MCB
There are a few differences between the RCD and MCB. Let’s disclose them.
Primary Purpose
The primary goal of the RCD device is to protect the human from electrical shocks. On the other hand, MCB protects the devices from the current surges.
Detection Setup
RCD detects the current leakage and cuts off the supply. In contrast, MCB is designed to detect the excessive current either due to overload or short circuit.
Trip mechanism
RCD uses a sensitive toroidal transformer to detect the current leakage. At the same time, MCB uses thermal and magnetic trip mechanisms for the detection of overloads.
Safety Focus
RCD focuses on the prevention of electrocution and fires, while the MCB saves circuit burnout and appliance damage.
Installation
RCD is installed before the MCB installation. The MCB is separately installed in the circuits to detect the current fluctuations and respond accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.Can you use MCCB in residential applications?
Technically, yes. If you have a large home setup with a high-voltage load, MCCB is preferred over the MCB. It can better handle the current flow and save your appliances from current damage
2.Why is it necessary to use an RCBO in the kitchen?
The kitchen is a high-risk area because of electrical, thermal, and water supplies. Therefore, RCBO provides all types of protection, ranging from short circuits to earth leakage, and prevents fire.
3.Can I use MCB instead of RCCB?
No. MCB circuit isn’t a suitable alternative for the RCCB as it can cover only the current surges while RCCB can handle current fluctuations with the leakage.
4.Can RCBO replace both MCB and RCCB?
Yes. RCBO can effectively replace the MCB and RCCB because of dual protection features.
Conclusion
Different types of circuit breakers are in the market. Some are ideal for commercial applications, such as MCCB, while others can work well at a small home, such as MCB. However, if you want added security at your home, deploy an RCD or RCBO. Select based on your needs.

