Circuit breakers are widely used in electrical automation, high and low voltage electrical equipment, and we often see them in civil buildings. This article will take you to learn more about their types, uses, functions, differences, etc., no matter you Technicians or novices, reading this article will have some reference significance for you.
What is Circuit Breaker
This is a circuit protection device used to protect circuits from problems such as overloads, short circuits, etc. When there is a problem with the circuit, it automatically cuts off the power supply to prevent further damage, protect the equipment and operators, and avoid losses. The circuit breaker will not cause damage to itself when it opens automatically, so it does not need to be replaced frequently.

Types of Circuit Breaker
Circuit breakers are essential safety devices in electrical systems. Use different circuit breakers in different scenarios. There are many types of circuit breakers with various voltages and currents. Roughly speaking, they can be divided into high-voltage circuit breakers and low-voltage circuit breakers. Generally, those exceeding 3KV are considered high-voltage circuit breakers. But how many types of circuit breakers are there that we need to know? The following are our common different types of circuit breakers:
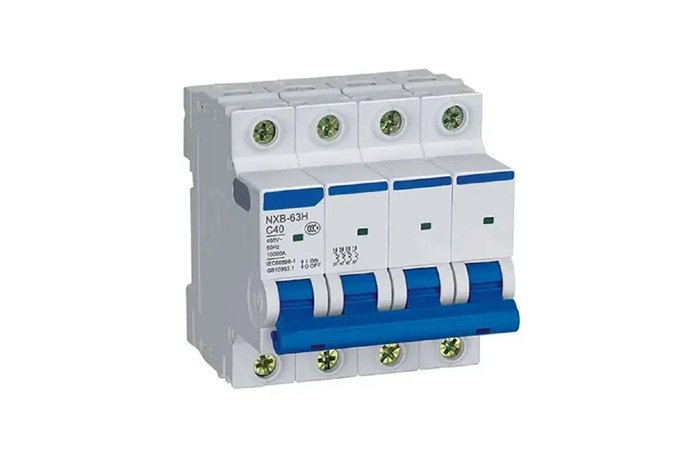
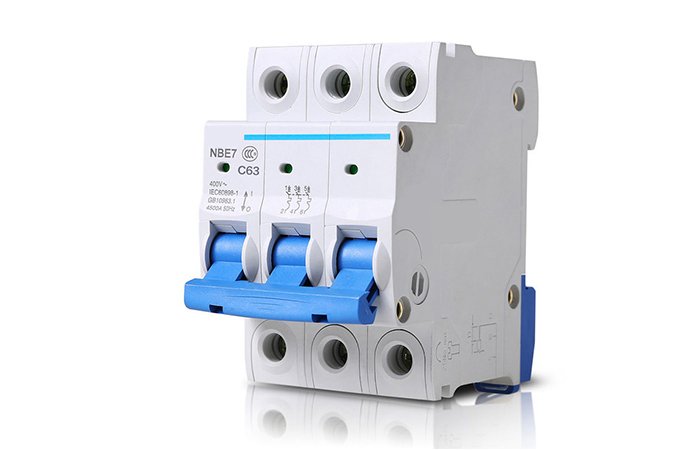
MCB
Miniature circuit breaker, mainly used for current overload and trip protection. According to voltage, there are AC and DC. Typically they have pole numbers: 1P, 2P, 3P and 4P. AC miniature circuit breakers are usually suitable for AC 50HZ/60HZ, voltage 400V, rated current below 63A, and circuit breakers used in homes, shopping malls, industries, etc. DC miniature circuit breakers are mainly suitable for DC circuits. Different poles correspond to different DC voltages. The current range is from 1A to 63A. The latest development can achieve 125A. DC miniature circuit breakers are widely used in solar systems, battery systems, and telecommunications equipment systems. The mini circuit breaker has strong breaking capacity, beautiful appearance and meets international standards.
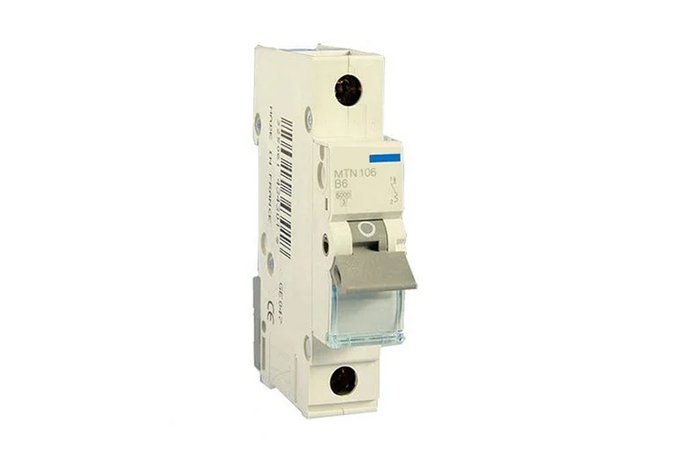

MCCB
Also a molded case circuit breaker. As the name suggests, all accessories come in a sealed plastic box. It is an overcurrent protection circuit breaker. Generally, opened by manual operation, and its rated voltage and rated current are higher than those of min circuit breakers. Rated current from 16A to 1600A and it can withstand uninterrupted system voltage. Molded case circuit breakers are small in size and competitively priced. The application of MCCB is very extensive,they are indispensable safety devices in distribution boxes.
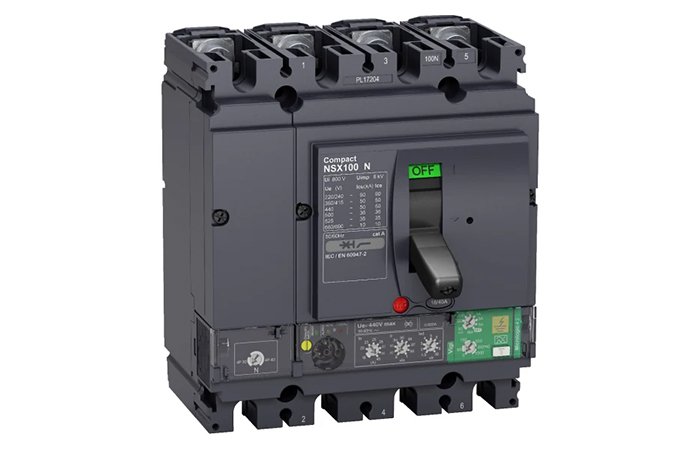

ACB
Also known as frame circuit breaker. All components of a frame-mounted circuit breaker are mounted within an insulating frame. A variety of accessories can be installed, and components such as contacts can also be replaced. The general rated current range is 630A ~ 6300A, which is mostly used in power distribution network systems. There are many types of overcurrent releases: electromagnetic releases, electronic releases and smart releases, as well as drawer types, mostly 3P or 4P. The air circuit breaker is large in size and has protection functions, measurement functions, auxiliary functions, special functions and communication functions.

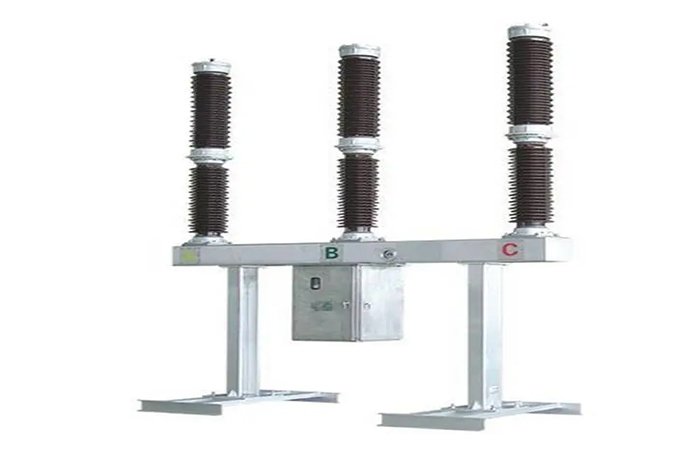
QF
It is a high voltage circuit breaker. It has strong arc extinguishing ability, which can prevent the accident from expanding and ensure safe operation when an accident occurs. The current of the high-voltage circuit breaker is 1500A-2000A, and these arcs can be stretched to 2M, so the arc extinguishing ability is the most important function of the high-voltage circuit breaker. High-voltage circuit breakers are suitable for handling high-voltage circuits, such as substations, high-voltage power grids, etc.

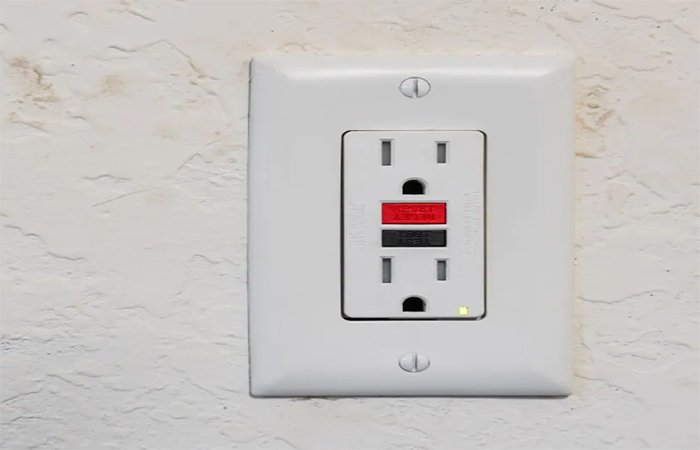
GFCI
Also known as ground fault circuit interrupter , this type of circuit breaker is suitable for humid environments that are prone to electric shock. It will quickly detect unbalanced currents on the live and neutral wires and quickly cut off the power supply to prevent the risk of electric shock or electric shock accidents. Compared with MCCB, GFCI responds faster.

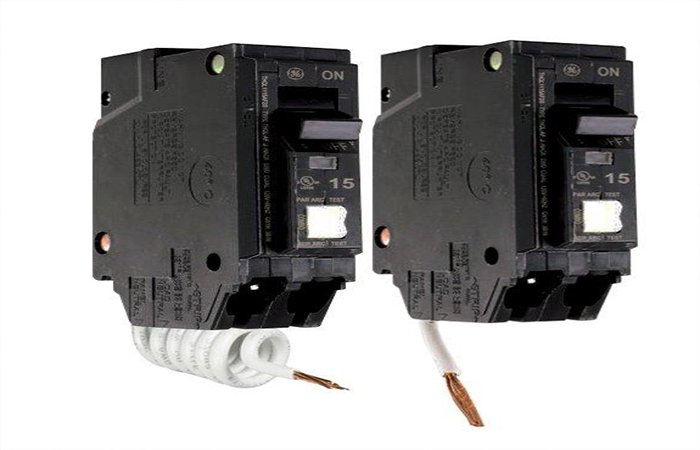
AFCI
Also known as Arc fault circuit breaker, this circuit breaker can detect abnormal arcs in the current and quickly cut off the power supply to prevent further expansion of the impact of the accident. This kind of circuit breaker can also add alarm function and improve the protection level of electrical fire.

In short, the types of circuit breakers are diverse. You can choose the proper circuit breaker type according to different use environments. If you want to know more information about the classification of the circuit breaker, you can search for more related articles.
Function of Circuit Breaker
Circuit breaker is an electrical device that acts as a protective umbrella for the entire circuit system. It plays an important role in protecting the entire equipment from further damage.The following are the main function of circuit breaker for your reference:
Overload Protection: When the current in the circuit exceeds the safe value of the circuit, the circuit breaker will automatically disconnect the power supply to prevent overload current from damaging the circuit and causing danger.
Current Short Circuit Protection: When an electrical fault causes a short circuit, the circuit breaker’s instantaneous function quickly cuts off power and prevents further damage, This is the basic function of circuit breaker.
Isolation: The circuit breaker can be used as a switch to isolate certain circuits without interfering with each other, making maintenance and operation more convenient.
Arc Extinguishing Function:How to isolate and extinguish long arcs between high-voltage power supplies.
In summary, circuit breakers also have long-delay, short-delay, instantaneous, and ground-fault capabilities. The diverse functions make circuit breakers highly sought after in the market.

Difference Between DC and AC Power
The choice of DC and AC depends on the needs of the specific equipment or application. The difference between the two mainly exists in the flow direction and voltage level:
Flow Direction:The flow direction of DC power supply is a fixed direction, which is a stable and balanced current. As the positive and negative poles of the voltage change, the direction of the alternating current will change accordingly. Generally, AC power is used in household electricity.
Voltage Level:The voltage level of DC is constant, while the voltage of AC changes with time, so AC is suitable for long-distance transportation with little loss, while DC is not suitable for long-distance transportation.
In summary, the electromotive force, voltage and current changes of DC and AC are different, but the specific application depends on the needs of the equipment.

Difference Between AC MCB and DC MCB
Let’s analyze the main differences between DC miniature circuit breakers and AC miniature circuit breakers. Understanding these differences will help you make better choices.
Different Voltage: the rated voltage of AC small circuit breaker is 220V/380V AC, and the maximum rated voltage of DC small circuit breaker is 4P 1000V.
Different Working Frequencies: The working frequency of AC MCB is 50HZ/60HZ, while DC MCB do not have this value.
Different Arc Extinguishing Ability: DC circuit breaker is not affected by resistance and has a strong ability to disconnect the circuit, while AC circuit breaker must have a rated capacity consistent with the voltage of the connected circuit to disconnect the circuit, so it has strong arc extinguishing ability but poor ability.
Different Breaking Capacities: AC miniature circuit breakers are more likely to break the circuit at zero point and therefore have lower breaking capacity than DC miniature circuit breakers, whereas DC miniature circuit breakers can handle the more challenging circuit conditions in DC circuits and have stronger breaking ability.
Different Applications: AC miniature circuit breakers are used to protect AC circuits and are often used in residential areas, commercial areas, etc.; DC mini circuit breakers are used in DC power supply applications, such as IT equipment, DC power supply systems, etc.
Conclusion: No matter what the differences and advantages between the two are, the specific use still depends on the specific circuit conditions.

Advantages of Circuit Breaker
As an electrical component, the circuit breaker has many advantages. The following points are the common advantages of circuit breakers:
Long life: The circuit breaker can withstand multiple sudden power outages and abnormal overload conditions, and has a relatively long service life.
Accuracy: The circuit breaker can accurately capture abnormal current in the circuit and respond quickly to disconnect the circuit.
Fire Protection Performance: When a circuit failure occurs, fire can only be prevented by disconnecting the circuit in time.
Compact Structure: The circuit breaker is small in size, and various parts are concentrated in the housing, occupying a small volume. Of course, miniature circuit breakers are smaller in size.
High Safety: Ground circuit breakers, fault arc circuit breakers, etc. provide leakage or arc protection to effectively prevent accidents.
Higher Stability: With powerful capabilities and compatible electrical parameters, as well as circuit breakers certified by international standards, the performance is safer and the work is more stable.
Convenience: Just push the lever up or down to open or close the circuit, no need to maintain the entire circuit system when power is on.
In essence, circuit breakers seem to be the Optimus Prime of electrical systems and have always existed as an indispensable electrical component in various industries.

How Do Circuit Breakers Work?
Circuit breakers are made up of many components. Let us see how they work together to make circuit breaker ON/OFF.
Current Sensing Mechanisms
Thermal Trip Element: Most thermal trip elements use a bimetallic strip made of two metals with different thermal expansion rates. When excessive current flows, heat builds up, causing the strip to bend due to uneven expansion. At a specific temperature (corresponding to a preset current threshold), the bending action triggers a mechanical latch, which opens the circuit.
The response time is inversely proportional to the overcurrent magnitude (higher current = faster trip). This allows temporary surges (like motor startups) without nuisance tripping but protects against sustained overloads.
Magnetic Trip Coil: It is a critical component in the circuit breaker that provides instantaneous protection against dangerous short-circuit currents. Its core function is to detect and respond to high-intensity short circuit currents (typically 5-30 times the normal current). It operates in 1-50 milliseconds — faster than thermal mechanisms and produces an instantaneous, force-based trip regardless of temperature.
Basic structure includes electromagnetic(coilcopper winding around an iron core), plunger/armature(movable ferromagnetic piece), trip latch( mechanical release mechanism) and adjustment screw(allows setting the trip threshold). Trip time varies with current magnitude (inverse-time characteristic)
The Contact System
The contact system is a crucial part of a circuit breaker, responsible for carrying current when closed and interrupting it when tripped. It ensures reliable operation under normal and fault conditions.
The components of a Circuit Breaker Contact System include below parts:
Fixed contact is a fixed part attached to the breaker frame, which is made of high-conductivity, arc-resistant materials (e.g., silver alloy, copper-tungsten).
Moving (arcing) contact moves to open/close the circuit which is designed to withstand mechanical wear and arcing.
The contact pressure spring ensures firm contact to minimize resistance and overheating and prevents contact bouncing during fault interruptions.
Arc chutes/arc extinguishing chamber splits and cools the arc during interruption using deionizing plates or gas (SF6, vacuum).
In high-current breakers, main contacts carry normal current and arcing contacts (made of harder materials) take the initial arc damage during opening.
Generally speaking, the internal parts of each type of circuit breaker are a little different, but the working principle of circuit breaker is similar. If you want to know more, see more articles.

Key Specifications and Ratings
Here are the critical parameters engineers must consider:
A. Rated Operational Voltage (Ue) is the maximum system voltage the breaker is designed for. Common Values include 120V, 240V (1-phase); 208V, 480V (3-phase) for residential, 600v, 690v for industrial and 4.16kV, 13.8kV, 33kV for medium Voltage.
B. Rated Insulation Voltage (Ui) is the voltage the insulation can withstand continuously, which is always higher than Ue (typically 1.25× Ue).
C. Rated Impulse Withstand Voltage (Uimp) is the lightning/surge voltage protection level, such as 6kV for 240V breakers.
D. Rated Current (In) is the maximum continuous current without tripping. The standard Series (IEC): 6, 10, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63, 80, 100, 125A.
E. Ultimate Breaking Capacity (Icu) is the maximum fault current the breaker can interrupt once. The typical values:
MCBs: 6kA-25kA
MCCBs: 25kA-100kA
ACBs: Up to 200kA
F. Service Breaking Capacity (Ics) is the current the breaker can interrupt multiple times (typically 25-100% of Icu).
G. Time-Current Characteristics
| Curve | Trip Range | Typical Applications |
| B | 3-5× In | Electronics, lighting |
| C | 5-10× In | Motors, transformers |
| D | 10-20× In | High inrush loads |
| K | 8-14× In | HVAC compressors |
| Z | 2-3× In | Semiconductor protection |
How to Use Circuit Breakers?
The use of circuit breakers includes three steps: how to select, how to install and how to maintain circuit breakers.
The first step is to choose the right circuit breaker. Select the type of circuit breaker according to the use environment, such as miniature or grounding circuit breaker. Determine the parameters of the circuit breaker according to electrical characteristics standards such as rated current and rated voltage, including circuit breaker ratings and specifications, and then determine the appropriate circuit breaker. Determine the number of poles according to the circuit that needs to be protected.
Next comes installation and wiring. Before installation, make sure the power is turned off to ensure safety, and then check whether the selected circuit breaker is consistent with the current parameters. The wiring methods of circuit breakers include front panel wiring, rear panel wiring, plug-in type, draw-out type, guide rail type, etc.
Installed circuit breakers do not need to be replaced frequently, but they must be inspected and maintained regularly. If the screws are loose, they must be tightened as soon as possible. If the circuit breaker is aged or the circuit breaker housing is cracked or burned, the circuit breakers must be replaced as soon as possible.
In short, the installation and maintenance of circuit breakers must be carried out in a safe environment and by professional people, improper behavior will lead to the risk of electrical accidents.

Application of Circuit Breaker
Circuit breakers are used in many situations, including buildings, shopping malls, industries, national power grids, etc. Both high and low voltages require circuit breakers. The following are some more common applicable environments:
- Industrial manufacturing: In industrial manufacturing and production environments, circuit breakers are used to protect important equipment from electrical faults without affecting the process of industrial production.
- Commercial buildings and residences: Circuit breakers can protect the building’s circuits from short circuits or overloads, ensure our daily electricity needs, and prevent fires and disasters.
- Solar system: DC small and large circuit breaker disconnects the fault current and protects the photovoltaic components in the solar system.
- Construction: Generally, there will be temporary circuit systems and construction equipment at construction sites, and circuit breakers can be used to protect these systems and equipment.
In addition to these occasions, circuit breakers have a wide range of applications.
FAQ
Are DC Circuit Breakers Directional?
Yes, it is directional and flows in a fixed direction.
Do Circuit Breakers Go Bad?
Yes. If the circuit is frequently short-circuited or the current load is often too high, the silver points of the circuit breaker contacts are easily worn and cannot carry the rated current, and the circuit breaker will be damaged.
Can AC MCB Use for DC?
No, the two cannot be used interchangeably.
Can I Change the Circuit Breaker by Myself?
No, you can’t. Replacing a circuit breaker is a relatively professional matter. If you don’t understand the principles of electricity, you can easily get electrocuted. Please arrange for a professional electrician to replace it.
How Do You Determine If this Circuit Breaker Needs to Be Replaced?
If there is a power outage to your home or electrical system, the first thing to do is to check whether the circuit breaker has tripped automatically. If other circuits are normal, the electrician will use an electric pen to test whether the circuit breaker is normal.