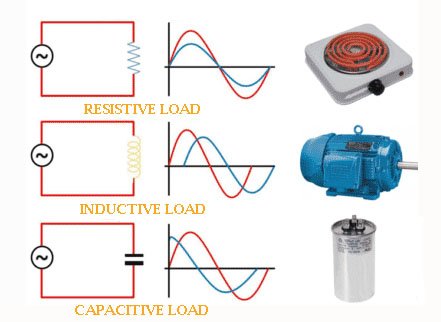
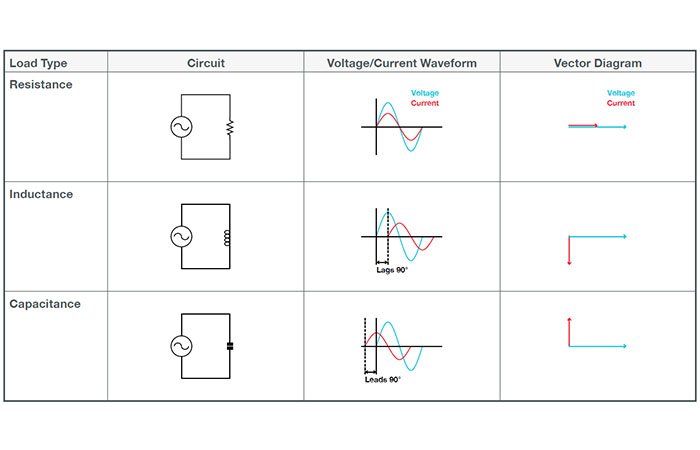
In any electrical system, you deal with different load types. Each load, inductive, capacitive, or resistive, responds differently to current and voltage. You must understand these differences to design stable and efficient circuits. This guide will take you through the practical differences between the three types.
Inductive Load
What Is Inductive Load?
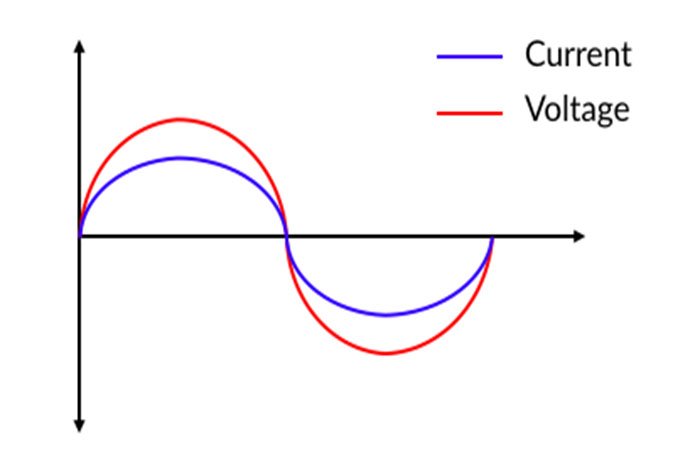
Inductive loads rely on magnetism to function. These are used in motors, solenoids, and transformers, all of which convert electrical energy into motion or force. An inductive load opposes an increase or decrease in current. They are coiled or wound. It’s done through the magnetic field generation around its coil. This implies that the current is always in lag with the voltage.
Considerations When Managing Inductive Loads.
Managing Inrush Currents and Voltage Spikes
Inrush currents can exceed normal load current many times. You should use ssoft starters or NTC thermistors to control this. For voltage spikes, apply snubbers or surge arresters across the load.
Power Factor Correction
Inductive loads reduce power factor by drawing reactive current. You can improve it using fixed or switched capacitors. This reduces losses and keeps your system within utility limits.
Circuit Protection and Load Switching
Inductive loads need fast, inductive-rated switching devices. Use magnetic contactors or solid-state relays with arc suppression to prevent arcing.
Industrial Applications of Inductive Loads
The following are inductive load examples:
- Electric Motors: These are used by motors in fans, pumps, and conveyors to create motion.
- Transformers: You may depend on transformers to adjust voltage levels in power distribution.
- Relays and Contactors: You use relays and contactors for switching loads automatically.
- Induction Heaters: You often use induction heating to warm metal parts without contact.
- Solenoids: You can install solenoids in valves and actuators to create linear motion.
Capacitive Load
What Is Capacitive Load?
A capacitive load stores energy in an electric field. It is used in capacitor banks, long cables, or power filters. It causes current to lead voltage, opposite to inductive loads. A capacitive load draws current before voltage rises, corrects power factor, and filters signals in electrical systems.
Where are capacitive loads commonly used?
Electronic Power Supplies and Filters
You can apply capacitive loads to stabilise voltage in a short period. They react more rapidly than inductive loads in circuits. They can store and release energy as opposed to resistance loads.
Motor Start Capacitors and Correction Banks
启动电容器用于辅助电机加速。它们在感性绕组响应之前提供电流。校正电容器组可立即帮助抵消无功功率。.
Renewable and Power Grid Applications
采用容性负载以稳定电网电压。在负载突变时,其响应速度比感性负载更快。与阻性负载不同,它们不会持续消耗能量。.
Challenges and Control of Capacitive Loads
Managing Overvoltage and Harmonics
使用容性负载可避免电压尖峰。它们能滤除开关或电源谐波失真。感性负载的存在会加剧因负载快速变化引起的谐波问题。.
Risks of Resonance in AC Circuits
使用容性和感性负载时应避免谐振。当频率匹配时,响应电压会产生尖峰。阻性负载永远不会引发谐振,但必须使用调谐滤波器进行处理。.
Load Balancing with Mixed Load Types
通过混合使用这三种负载来实现系统平衡。容性负载补偿感性设备引起的相位滞后。阻性负载稳定电流,但不调节相位。.
Resistive Load
What Is Resistive Load?
在产生热量的系统中使用阻性负载。它们将电能无延迟地转化为热能。电压和电流保持完全同相。能量不会随时间储存和释放。.
Practical Examples of Resistive Loads
Heating Elements in Industrial Equipment
基于恒定热输出需求采用电阻加热。它是一种快速响应的开关设备,无滞后或超前。感性加热器需要控制系统,而阻性加热器则不需要。容性类型不适合直接传热。.
Incandescent Lighting and Electric Ovens
可依赖阻性负载提供照明和热量。. 白炽灯泡 无延迟地将能量转化为光。烤箱加热均匀,不受无功电流影响。感性和容性负载无法匹配这种简洁性。.
Load Banks for Testing and Simulation
为模拟实际阻性需求,需使用负载柜。它们有助于测试发电机、UPS和电源单元。不存在无功行为,从而确保正确可靠的结果。.
Benefits of Resistive Loads
Stable Output
在稳定电压输入下获得一致响应。无能量存储意味着零延迟或失真。感性负载导致滞后;容性负载导致超前。阻性负载保持精确的电流流动。.
High Efficiency
可将几乎所有电能转化为有用热能。不存在磁场或电场引起的损耗。感性系统因磁场建立而损耗能量。而容性类型也会浪费无功功率。.
Easy Setup
安装阻性负载无需复杂控制或调谐。不需要滤波或补偿装置。感性负载需要软启动和电弧保护。相比之下,容性装置需要相位平衡调整。.
How to Use Inductive, Capacitive, and Resistive Loads
Proper Wiring
必须使用标准保护装置连接阻性负载。相移或无功能量不会影响布线。感性负载需要慢熔保险丝和耐电弧开关。容性负载需要浪涌保护和放电路径。.
Load Matching
必须根据系统电压和功率确定负载规格。阻性负载消耗稳定电流,其规格计算简单。感性负载需为涌流预留额外余量。容性负载需要无功平衡以避免谐振。.
Safety Measures
应在电阻加热设备上安装热熔断器。感性负载应使用电弧抑制和软启动器。容性负载需要放电电阻以耗散储存电荷。开关行为应始终用真实负载进行测试。.
Inductive Loads vs Capacitive Loads vs Resistive Loads
| 因素 | Inductive Load | Capacitive Load | Resistive Load |
| 能量存储 | 磁场 | 电场 | 无 |
| 电流-电压相位 | 电流滞后电压 | 电流超前电压 | 电流与电压同相 |
| 功率因数影响 | 滞后(低) | 超前(低) | 单位功率因数(1.0) |
| 启动特性 | 高涌流 | 瞬时超前电流 | 稳定即时消耗 |
| 系统风险 | 反电动势、电压尖峰 | 谐振、过电压 | 过载发热 |
| Common Use | Motors, transformers | 校正电容器组、滤波器 | 加热器、灯具 |
Conclusion
总体而言,感性、容性和阻性负载在交流电源下具有不同的特性。每种负载类型都会影响功率因数、开关行为和保护策略。了解这些特性后,可验证负载选择是否恰当、布线是否安全以及系统设计是否最优。.
FAQ’s
Q1:能否在同一系统中组合不同类型的负载?
可以组合这些负载类型。但必须保持无功和有功分量的平衡,以避免不稳定或谐振。.
Q2:为什么容性负载导致超前功率因数?
容性负载瞬时释放储存电荷。这导致电流在电压建立之前流动,从而产生超前功率因数。.
Q3:阻性负载在交流与直流下的行为如何? 交流与直流?
阻性负载在交流或直流下表现相同。与无功负载不同,它们消耗恒定电流且不产生相移。.
Q4:感性负载是否始终需要软启动器?
并非总是需要,但对于大功率感性负载,建议使用软启动器以限制涌流并减少机械应力。.