The electrical system deals with the current and voltage. Sometimes, a surge of current or voltage in the circuit can cause damage to the devices if they are not rated to handle the spikes.
Two protective mechanisms emerge that cut off the supply and protect the appliances at home or in industrial sectors.
We will discuss fused disconnect switches vs. circuit breakers and understand their differential points.
What is A Fused Disconnect Switch?
A fused disconnect switch provides manual physical disconnection of current or voltage by the user. Additionally, it incorporates a fuse system to interrupt the supply for overcurrent protection.
Whether due to a short circuit or overload, these switches ensure system protection.
Features include:
- Provides both manual isolation and fuse protection.
- Protects equipment from overcurrent by blowing the fuse when current exceeds safe limits.
- Ensures safety during maintenance and repairs.
Fused Disconnect Switch Types
The fused disconnect switch is available in three configurations, which determine the overcurrent or short circuit protection.
Fusible
These types of disconnect switches include a fuse configuration that provides overload or short circuit protection along with manual disconnection.
Non-fusible
They do not incorporate a fuse and are primarily used as a disconnection device. Only physical circuit disconnection occurs.
Enclosed safety switch
Enclosed safety switches feature a rugged enclosure designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions and operate reliably outdoors.
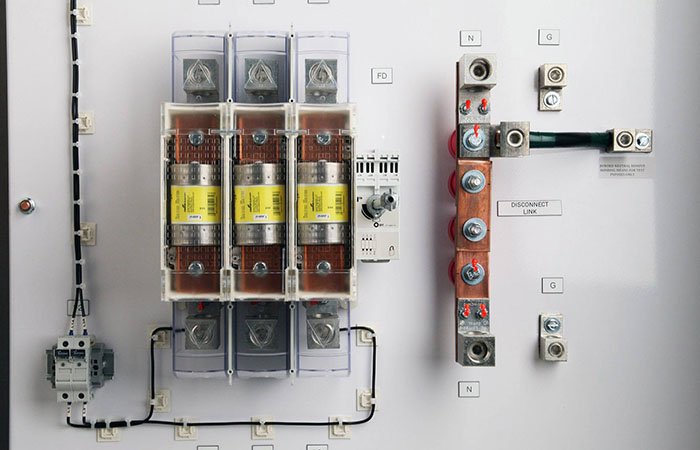

What is A Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is an automated device for disconnecting voltage or current. It detects changes in electrical current and protects appliances by disconnecting them.
A circuit breaker is effective for residential or commercial applications due to its automated operation. Key features are:
- Provides automatic switching during faults.
- It can be reset manually or automatically after tripping.
- Protects against a wider range of faults compared to fused switches.
Circuit Breaker Types
There are several types of circuit breakers.
Miniature Circuit Breaker
MCBs have a compact structure and current ratings up to 125 A. They are ideal for low-voltage applications and provide reliable protection against overload or short circuit.
Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Molded case circuit breakers are suitable for large-scale settings, capable of handling currents up to 1600 amps. They offer extended protection against current and voltage surges.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter
The GFCI type of circuit breaker interrupts the circuit by detecting current leakage. It prevents electrical shocks through proper management.
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter
Arc fault circuit interrupters detect potential failures that could cause fires in the system. They provide enhanced surge protection and efficiently safeguard devices.

Key Differences Between Circuit Breakers and Fused Disconnect Switches
Circuit breakers operate differently compared to disconnect switches. Several key differences are outlined below.
Protection Method: Fuse vs Resettable Mechanism
A fused disconnect switch incorporates a fuse mechanism. When the load exceeds rated limits, it indicates danger and physically interrupts the current flow. Fuses blow when a specific limit is exceeded.
In contrast, a circuit breaker resets its settings and cuts off the current supply in case of overload. Replacement is unnecessary, as the tripped mechanism can be reset.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
A fused disconnect switch has a lower initial cost but requires long-term maintenance and incurs ongoing expenses, as fuses must be replaced periodically, leading to increased costs over time.
A circuit breaker has a higher upfront cost but does not require significant maintenance investment, as it automatically resets the system without replacement expenses.
Response Time to Faults
A fuse provides an instantaneous and timely response by sacrificing itself without damaging operating devices. It is ideal for sensitive applications where surge protection is critical.
Conversely, circuit breakers offer comprehensive protection but with a slightly slower response time. The choice should be based on application requirements.
Resetting vs Replacement After Trip
What is your preference? Resetting allows you to restore settings after each use. A fuse requires replacement after each operation, as it is damaged upon activation.
In comparison, circuit breakers provide comprehensive protection over extended periods without replacement. Automated reset functionality offers superior protection.
Typical Applications in Electrical Systems
Fused disconnect switches are the preferred choice for industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and heavy equipment.
Circuit breakers are suitable for residential, commercial, and large distribution systems.

Which One Is the Best Solution for Your Application
Selection depends on the specific application requirements of your system.
Match device to application needs
What types of devices do you have? Ultra-sensitive devices require instantaneous response, and a fuse mechanism often provides the necessary speed for protection.
Define the protection mechanism you need
Can you manage replacement costs? If yes, a fused disconnect switch may be suitable. Otherwise, consider a circuit breaker system, which does not require replacement.
Safety and code compliance
Local electrical codes also dictate the protection mechanisms to be deployed. In residential settings, AFCI and GFCI breakers are increasingly mandated to mitigate fire and electrocution risks.
FAQs
1. Is it ideal to replace a circuit breaker with a fused disconnect switch?
Not always. A fused disconnect switch does not offer reset functionality to ensure system longevity. Therefore, replacing a circuit breaker with a disconnect switch is not recommended.
2. Do Circuit Breakers Last Longer than Fuses?
Yes. Circuit breakers last longer because of the resetting mechanisms once they trip. The fuse disconnect switch gets its fuse blown after every use.
3. How is a fused switch different from a non-fusible switch?
Fusible switches have a fuse protection mechanism, while the non-fusible switches are only disconnection devices.
4. Should a chief switch be a circuit breaker?
In major systems, we can say yes. It is because a chief switch should provide the ultimate protection with longevity. Only the circuit breaker can make it happen.
Conclusion
A circuit breaker is good at various tasks, while a fused disconnect switch is at another. However, a fused disconnect switch provides fast and reliable physical disconnection compared to an automated circuit breaker reset system.