Автоматический выключатель постоянного тока Langir для решения проблемы подключения солнечных батарей.
Высококачественные материалы для ваших автоматических выключателей постоянного тока!
- Прочная литая изоляционная оболочка
- Механизм быстрого включения или выключения с помощью рукоятки
- Электромеханический или электронный компонент отключения
- Тип JB, предназначенный для многоканальных фотоэлектрических установок
- Дополнительная защита цепей постоянного тока от перегрузок и короткого замыкания
Автоматический выключатель постоянного тока Langir: сверхнадежная работа 24/7
Автоматический выключатель постоянного тока Langir — это очень надежный выключатель, которому вы можете полностью доверять.
Скачки напряжения, перегрузки, электрические неисправности и короткие замыкания — это лишь некоторые из проблем, с которыми мы сталкиваемся сегодня при работе с электрическим током. Без надлежащей защиты наши электроприборы могут сгореть или повредиться, и их ремонт, скорее всего, будет невозможен. Если вы владеете бизнесом, ваши активы могут оказаться под угрозой, и вы можете понести огромные финансовые потери.
Восторженные отзывы по всему миру



- Фабрика
- Команда
Команда
FAQ'S
The Langir’s DC circuit breakers are specially built to protect connected cables which are connected to your appliance or other electrical devices.
You can choose from 1 pole, 2 poles, 3 poles, and 4 poles DC circuit breaker types.
Langir’s DC circuit breakers have 1 amp, 2 amps, 3 amps, 4 amps, 6 amps, 10 amps, 16 amps, 20 amps, 25 amps, 32 amps, 40 amps, 50 amps, and 63 amps.
Yes, although Langir’s DC circuit breakers are built with high quality and precision, you will be provided with product liability insurance and a warranty of up to 365 days.
Langir delivers fast in just 2 to 3 days period after your order is confirmed but ensuring that your order or orders are received in good condition.
Langir DC Circuit Breaker
Langir is your leading supplier of reliable DC circuit breakers from China.
With decades of solid experience in the industry, Langir is an expert in DC circuit breakers whether for your home or your business.
If you are in search of the best supplier of DC circuit breakers, Langir must be your first choice of manufacturer.
Langir offers single pole, double pole, three poles, and four poles DC circuit breakers so you have more options.
Our DC circuit breakers also offer different amp ratings from 1 amp up to 63 amps with voltage ratings from 250 volts up to 1000 volts.
The easy snap-in mounting provides simple and quick installation saving time and cost for professional fees.
Langir DC circuit breakers are compliant with TUV Rheinland and approved by SAA.
And also conforms to the international standards IEC 60947-2, EN60947-2, and GB 14048.2.
Our DC circuit breakers are widely used for homes, businesses, factories, and for specific electrical devices that must be protected from short circuits and overloading.
With our DC circuit breakers, you are guaranteed that your appliance and other devices or equipment connected with it will have a long life and will keep their optimum performance for generations.
Langir greatest happiness is to cater to your needs and support your growing business.
Contact us for a free quote.
DC Circuit Breaker – FAQ Guide
In our guide for DC circuit breaker, you will discover what it is all about, its amazing purpose, and the applications where it is used.
You will also learn a piece of its interesting history as this guide will take you back in time to the important events that lead to the discovery of DC circuit breakers.
Moreover, this guide will also provide you with crucial information on the comparison between DC circuit breakers, AC circuit breakers, as well as fuses.
More importantly, you will learn the different standard codes which will give an in-depth understanding of how governing bodies put your safety first.
You’ll also be guided on the things you need to consider when choosing DC circuit breakers and their advantages.
So if you’re planning to purchase one, read our helpful guide first that we’ve put together just for you.
1. What is a DC circuit breaker?

DC circuit beaker
A DC circuit breaker is an operational electrical switch made to automatically prevent an electrical circuit from getting damaged by excess current due to a short circuit or overloading.
The DC stands for the direct current which is defined as an electric current that runs in one direction only.
It is also known as DC-rated circuit breakers or circuit breakers for DC power supply.
Its fundamental function is to interrupt current flow upon detecting a fault, a feature also referred to as OCPD (Overcurrent Protection Device).
A DC circuit breaker operates once and typically requires resetting to resume normal functionality.
DC circuit breakers are available in various sizes, including compact units designed to protect low-current circuits (e.g., for individual household appliances).
The price of a DC circuit breaker can range from $10 to $30 or more, depending on its type, size, and configuration.
Fun Fact: There was once a "battle of currents" that lasted nearly a decade and even inspired a film!
During the 1880s to early 1890s, the “War of the Currents” (also known as the “Current War”) became the most notable conflict over electrical currents in human history.
This refers to a series of events between Thomas Edison and George Westinghouse regarding which electrical power transmission system would be adopted in the United States.
The events of the Current War were so significant that Hollywood produced a film of the same name in 2017.
In 1878, Thomas Edison recognized the market potential of supplying electricity directly to homes and businesses.
Consequently, he developed a DC lighting system based on 110-volt direct current, a relatively low voltage to power the high-resistance incandescent lamps he invented for the system.
However, the primary drawback of the DC lighting system was its limited transmission range, capable of delivering usable power only within about a mile from the generating plant.
This meant that residents and businesses located more than a mile from the plant experienced weak, unstable, or no electricity at all.
In 1885, after learning of new European AC transformer systems, Westinghouse developed a lighting system based on alternating current.
Two years later, the first AC power system with incandescent lighting was installed in Great Barrington, Massachusetts.
This multi-voltage power system could supply electricity to up to 23 businesses along Great Barrington's main street.
It used transformers to step down 500 AC volts to 100 volts to power incandescent lamps—a lower voltage than the DC lighting system.
In 1886, he established the first commercial AC power system in Buffalo, New York.
Thus, two electrical power transmission systems began competing for dominance in the same city.
At the height of the Current War, Edison denounced alternating current following the death of a lineman electrocuted while working on a lighting pole with AC power lines.
The proposed solution was to bury high-voltage lines underground, but Edison opposed it, arguing that it would endanger more lives.
He advocated for limiting AC voltage and vowed never to use AC as long as he led his company (later Edison General Electric).
One publication even claimed there were 87 deaths related to AC high voltage.
Westinghouse refuted this, stating that his household AC transformer system used lower voltages than direct current, with only five accidental electrocutions and no in-home fatalities.
The war did not end until 1890, when Edison left his company to focus on iron ore refinement projects, which consumed most of his time.
After his departure, his former company began producing AC-based equipment and even removed Edison's name from the company title—a change he was unaware of until it occurred.
Fifteen electrical companies were involved in this decade-long Current War, but through mergers over the years, only two remained dominant: General Electric and Westinghouse.
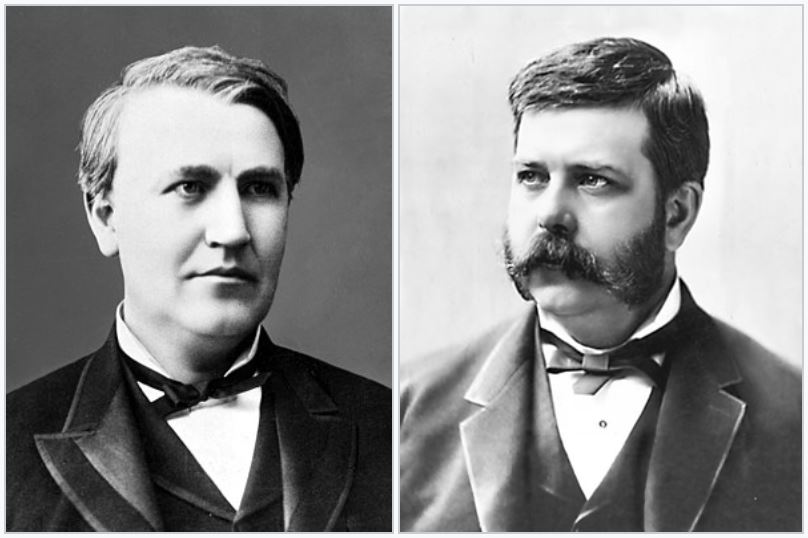

Thomas Edison and George Westinghouse
2. What is the development history of the DC circuit breaker?
In 1879, Thomas Edison conceived the idea of a circuit breaker.
At that time, electrical networks were being rapidly deployed across many industries.
This included electric lighting.
Edison recognized that short circuits frequently occurred during the widespread installation of lighting in major cities.
Such incidents would damage bulb filaments irreparably, and the costs of replacement and pole repairs were substantial.
He devised two methods to mitigate short circuits:
- The first was to use a wired fuse that would self-destruct during a high-current surge.
- The second was to employ a mechanical device that would spring open upon detecting excessive current.
The contacts of this mechanical device could be manually reset.
He sketched numerous designs for fuses and circuit breakers in his scientific journals and patented the concept that same year.
Ultimately, however, Edison chose to use fuses.
From 1876 onward, continuous innovations began improving the initial models.
Around this time, Edison established an industrial research laboratory where he worked on new inventions.
In 1898, the first circuit breaker was installed at the Boston Electric Light Company's L-street station.
It featured upward-breaking contacts that were manually activated and an oil tank.
The oil helped dissipate heat generated by the arc formed between the two open contacts.
In 1900, Granville Woods invented the automatic circuit breaker.
He was an African-American inventor who contributed many advancements to the railroad industry.
Woods gained fame for developing a method enabling train stations to communicate directly with train conductors.
The first company to mass-produce circuit breakers was the Cutter Manufacturing Company in Philadelphia in 1904.
Marketed as the ITE breaker (Inverse Time Element), it achieved great success.
Today, various iterations of ITE breakers are still available.
For forty years, electricians and installers followed their own standards for circuit breakers and specifications.
It was not until 1922 that AIEE Standards No. 19 was established, defining maximum heat limits for circuit breakers and prohibiting fire-hazardous devices.
DC circuit breakers were developed later.
Over a century later, many modern electrical systems are equipped with DC circuit breakers.
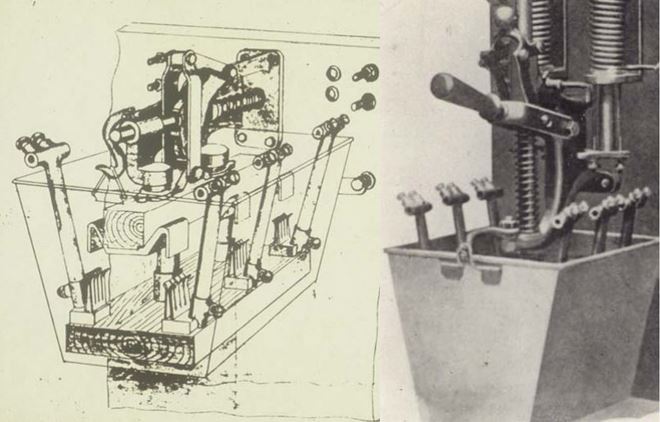
1898 oil breaker
3. To understand DC circuit breakers, how does electricity work?
To properly comprehend DC circuit breakers, one must first understand how electricity functions.
Certain properties define direct current (DC).
It involves negatively charged particles called electrons being converted into positively charged particles.
Electricity is generated when these electrons flow through a conductor, such as a copper or aluminum wire.
As previously mentioned, direct current flows in only one direction, meaning the positively charged electrons move unidirectionally.
4. How does a DC circuit breaker operate?
Generally, circuit breaker systems share common operational features, but specific details vary significantly based on current rating, voltage class, and breaker type.
At this point, we know that DC circuit breakers protect the electrical circuit, including other devices that use the power supply, from damage.
DC circuit breakers operate when they detect that the circuit is at risk of becoming overloaded.
When a fault is detected, they quickly interrupt the electrical connection.
For example, a power strip has a built-in circuit breaker.
If too many devices are drawing power from a single source, the DC circuit breaker shuts off the power.
Thus, it protects the electrical devices plugged into the power strip.
This is commonly used with desktop computers.
A CPU can be damaged by a sudden power surge, which is why a power strip protects it with a built-in DC circuit breaker.

CPU circuit breaker
5. Are there different ways for DC circuit breakers to reset?
Yes, some DC circuit breakers are designed to reset in three ways:
- Manual DC circuit breakers
Once a manual DC circuit breaker trips, if you are nearby, you will likely hear a click and the power supply will be cut off.
In a residence, when this occurs, you would inspect the electrical panel.
This is the metal electrical service distribution box, which may contain several DC circuit breakers depending on the number of electrical circuits distributed throughout your house.
You will find one or more DC circuit breaker levers flipped; if you have sufficient knowledge of electrical circuits, you can investigate the cause of the problem.
Typically, you need to unplug appliances and other connected devices before manually resetting the DC circuit breaker, or returning the lever to its normal position.
This ensures that power is gradually restored to the areas of your home where it was lost.
It also helps identify which appliance may have caused the circuit overload.
- Automatic DC circuit breakers
Automatic DC circuit breakers are built to reset automatically.
When they trip, as the internal components cool down, they will attempt to reset the circuit or cycle.
- Modified DC circuit breakers
Modified DC circuit breakers are also referred to as trip-and-hold or modified reset breakers.
The shortstop breaker cools down, and then the internal electrical contacts attempt to reconnect, automatically resetting the circuit breaker.
If overloading or a short circuit persists, the DC circuit breaker will trip again and repeat the cycle until the issue is resolved.
Different types of DC circuit breakers in a fuse box
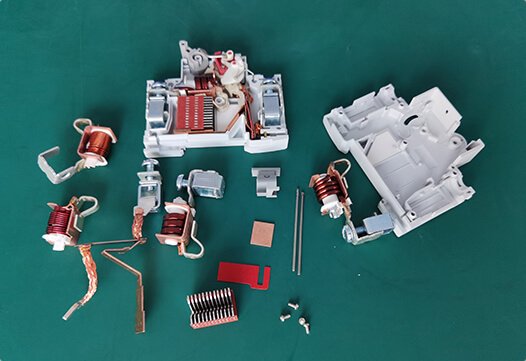
6. What are the main components of a DC circuit breaker?
The parts of a DC circuit breaker may vary by type, but the main components are generally the same for most, though manufacturers may label them differently.
The following are the commonly known main components of a DC circuit breaker.
- Molded case – The enclosure that houses the DC circuit breaker's internal parts and holds its components together. It consists of a base and a molded cover.
- Operating handle – A spring-assisted movable lever used to turn the DC circuit breaker on/off and reset it.
- Trip button – This allows mechanical tripping of the DC circuit breaker and is typically used to test the device.
- Terminals – Points where incoming and outgoing loads are connected.
- Contacts – Consist of moving and static contacts that separate during a short circuit or overload.
- Overcurrent tripping device – A mechanism that detects overcurrent and causes the breaker to trip.
- Arc extinguishing device – A device that instantly quenches arc formation.
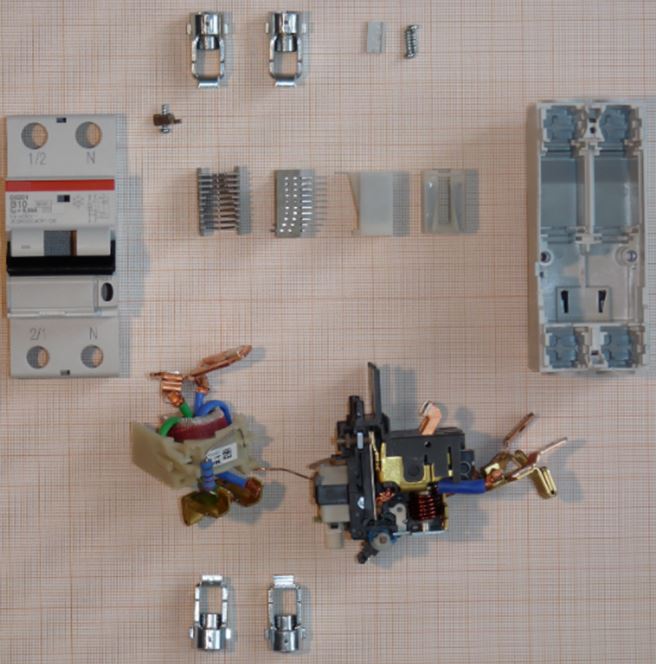
Parts of the DC circuit breaker
7. What materials are used to make the DC circuit breaker's frame?
The circuit breaker's frame ensures that all vital components are securely held in place for proper operation and appropriate mounting.
The frame's mechanical strength must be sufficient to withstand potentially large and damaging currents.
The circuit breaker's frame should also provide insulation and separation of the current path, thereby protecting anyone near the equipment during operation.
It is also one of the factors that help the DC circuit breaker comply with standard codes.
There are two types of DC circuit breaker frames:
- Metal frame
Metal pieces are precisely cut, bolted, and welded together to create the frame for DC circuit breakers.
Older DC circuit breakers may be housed in metal frames.
In fact, historically, all DC circuit breakers below 600 volts were once called metal-frame circuit breakers.
Metal frames are still used for DC circuit breakers with higher voltages today.
- Molded insulating material
Most molded insulated frames are specially made from robust insulating materials such as thermoset composite resins or glass polyester.
These types of frames are generally used for low-voltage DC circuit breakers, with sizes based on their ampere ratings.
For example, for 12V DC circuit breakers, 12-volt DC circuit breakers, 24V DC circuit breakers, 24-volt DC circuit breakers, 48V DC circuit breakers, or 48-volt circuit breakers.
They are also found in insulated case circuit breakers.
However, due to advances in materials and technology, molded insulated frames are now used for circuit breakers with 600 volts or higher, such as DIN rail DC circuit breakers, 1000V DC circuit breakers, or 1000-volt circuit breakers.

Old circuit breakers
8. What is the contact type inside a DC circuit breaker?
In a DC circuit breaker, the contacts provide a means to connect the circuit to the unit and to separate part of the circuit from other parts of the unit.
As mentioned earlier, contacts consist of fixed and movable contacts.
When the DC circuit breaker opens or closes, the movable contact moves to open or close (break or make) the circuit.
Operating the contacts requires a specific operating mechanism.
This can be purely mechanical or a combination of power and mechanical components.
Depending on the type of circuit breaker, the operating mechanism can:
- Manually open and close the contacts
- On-demand opening and closing of contacts
- Automatic opening of contacts
Regardless of their size, DC circuit breakers require assistance to actuate the operating mechanism for opening or closing the contacts.
This is where the spring comes into play.
Springs play a major role in opening or closing the contacts, aiding the circuit breaker mechanism to function precisely.
They are either relaxed or compressed to deliver the mechanical energy required for the opening and closing of the contacts.
Typically, there are two types of spring-assisted operating mechanisms:
- Manual over-toggle
Manual over-toggle is also referred to as quick-break or quick-make type.
The speed of this operating mechanism depends on how fast the handle is moved.
Motor operators are used to automatically actuate the handle in the absence of manual operation.
The handle is moved to open or close the circuit breaker until it reaches its extreme position, hence termed over-toggle.
Then the spring-assisted device automatically opens or closes the circuit breaker.
The design of the manual over-toggle allows the circuit breaker to trip open when necessary, even if the handle is set to the closed or “on” position.
- Two-step stored energy
This is employed when a considerable amount of energy is required to promptly close the circuit breaker.
The closing spring is charged, and the energy is released to close the breaker.
It is designed with separate springs for opening and closing the circuit breaker, allowing the closing spring to move independently during the opening process.
This also enables an open-close-open cycle.
The motor can be activated remotely; it features quick reclosing with stored energy in a separate closing spring and provides safety due to the isolated charging of the spring.

DC circuit breakers in a control cabinet
9. What is the trip unit inside a DC circuit breaker?
A trip unit functions as the intelligence of a DC circuit breaker.
A DC circuit breaker requires a certain level of intelligence to automatically respond to commands; otherwise, it would merely be an elaborate switch.
The purpose of the trip unit is to “trip” or open the circuit when overcurrent conditions occur, such as short circuits, thermal overloads, and ground faults.
Generally, trip units are of two types:
- Electromechanical trip unit (thermal-magnetic)
The electromechanical trip unit is commonly used in low-voltage circuit breakers.
It is integrally mounted into the circuit breaker and is temperature-sensitive.
Thermal tripping occurs during overloads: the load current heats the bimetal element, and with sustained overload, the bimetal deflects, thereby tripping the operating mechanism.
Magnetic tripping occurs when the current rapidly increases as it passes through the magnetic field, causing the electromagnet to attract the armature, thus tripping the DC circuit breaker.
- Electronic trip unit
The electronic trip unit consists of three internal components: the circuit board, current transformer, and flux-transfer shunt trip.
The circuit board acts as the system's brain, interpreting the input current and making decisions based on set parameters.
The current transformer continuously monitors and reduces the current to the appropriate input level.
The decision to trip directs output to the flux-transfer shunt trip, thereby causing the DC circuit breaker to trip.
Old thermal-magnetic interrupter on a motor circuit breaker
10. What are the similarities and differences between AC and DC circuit breakers?
The DC circuit breaker is a relatively new technology.
Most households use AC and, therefore, employ AC circuit breakers.
However, aside from their differences, both also share similarities.
Here are some comparisons between AC and DC circuit breakers:
- Voltages
DC circuit breakers are used with programmable logic controllers rated at 24 VDC and 48 VDC, as well as in applications such as wind power systems.
AC circuit breakers, in general, are rated to interrupt currents beyond 6 kA.
Some manufacturers offer dual-rated circuit breakers; this means one unit is suitable for both AC and DC, with ratings from 48 VDC to 125 VDC.
- Operation (arcing issues)
AC and DC circuit breakers appear similar in design and function similarly, but their internal operations differ.
During an overload, the internal contacts of both separate to protect the circuit.
However, throughout the period when the contacts are separating, an arc is formed.
This arc is the current that jumps across the gap and is referred to as contact arcing.
Contact arcing occurs when circuit breakers are opened or closed.
This arc must be extinguished immediately; otherwise, it will continue to jump across the gap, and current will keep flowing through the circuit.
When it comes to extinguishing the arc, AC and DC circuit breakers operate differently.
AC circuit breakers are not designed to handle the arcing issues associated with DC circuit breakers, which is why they are not interchangeable.
DC circuit breakers are specifically designed to address arcing problems and incorporate additional measures to quickly disperse the electrical arc formed during circuit opening and closing.
This is also known as DC arc suppression.
- Protection mechanisms
Both AC and DC circuit breakers share the same working principle regarding their thermal and magnetic protection mechanisms.
These protection mechanisms trip both circuit breakers when they detect high current loads, current faults, or short circuits.
- Versions
Both AC and DC circuit breakers are available in DC miniature circuit breaker and molded-case versions.
Miniature versions handle currents below 100 amperes, while molded-case versions are typically larger and may feature adjustable protection settings.
- Physical installations
The physical installation of DC circuit breakers shares many similarities with that of AC circuit breakers.
DC circuit breakers feature a simpler wiring method compared to AC circuit breakers.
DC circuits are wired to a fuse box, where cables are typically protected by adequate metallic or plastic conduits.
This circuit can be directly connected to the DC device and controlled by a switch, or it can also be plugged into an electrical outlet.
DC circuit breakers are connected in series along the live conductors for each circuit.
This is where AC differs, as it can have up to three live conductors, each serving a different purpose and requiring connection to the correct pole of the circuit breaker.
This can lead to connection errors, potentially causing electrical accidents or causing motors to operate in the opposite direction.
In direct current systems, all applications use only one live conductor.
There is zero risk of confusion with connections.
There may be other similarities and differences between AC and DC circuit breakers not listed here, but the key point is that both have advantages suited to specific applications.
How do you compare fuses and DC circuit breakers?
Any building using electricity requires the installation of DC circuit breakers.
Even if fuses are already installed, DC circuit breakers are still necessary.
They prevent power surges and avoid the constant blowing of fuses.
Similarities between fuses and DC circuit breakers:
- Both serve the same purpose, providing short-circuit and current overload protection.
- Both can be installed inside a fuse box.
Differences between fuses and DC circuit breakers:
- DC circuit breakers can be reset, whereas a blown fuse must be replaced.
- They may provide the same circuit protection but operate differently:
- Fuses blow and cut off the circuit when accumulated heat reaches the melting point, thereby protecting against overload.
- DC circuit breakers rely on the magnetic effect for short-circuit protection and the thermal effect for overload protection.
- Using DC circuit breakers is more cost-effective than repeatedly replacing blown fuses.

Different sizes of fuses and a blown fuse.
What should you consider when choosing the right DC circuit breaker?
There are important factors to consider when selecting the appropriate DC circuit breaker.
Considering these factors will facilitate installation and prevent future issues.
Here are some aspects to consider:
- Size of the DC circuit breaker.
The size of the DC circuit breaker depends on the scale of the unit it is intended to protect.
For example, for individual appliances, a small DC circuit breaker, such as those in power strips, can be chosen.
However, for powering multiple neighborhoods, large switchgear is required to protect high-voltage circuits.
- Type of protection mechanism.
DC circuit breakers feature both thermal and magnetic protection.
Thermal protection safeguards the circuit when it detects a current exceeding the rated value.
It is based on a bimetallic component that heats up, expands, and triggers the DC circuit breaker.
As the current increases, it operates faster due to greater heat generation, which expands and opens the electrical contact.
Magnetic protection triggers the DC circuit breaker instantly upon detecting a high fault current.
This is based on the rated breaking capacity of the DC circuit breaker, which indicates the maximum fault current it can interrupt.
Since the interrupted current is constant, it requires a wider opening of the electrical contact to interrupt the fault current.
Magnetic protection also guards against short circuits, which are significantly larger than overloads.
It is crucial to ensure the circuit breaker specifications are compatible with the electrical supply current type; otherwise, it may not protect the circuit effectively, potentially leading to electrical accidents.
- Electrical wiring with adequate rated current.
The wiring connecting the electrical device and the DC circuit breaker should have a sufficient rated current.
Even with the correct DC circuit breaker, undersized wiring can overheat, causing insulation to melt and leading to electrical faults.
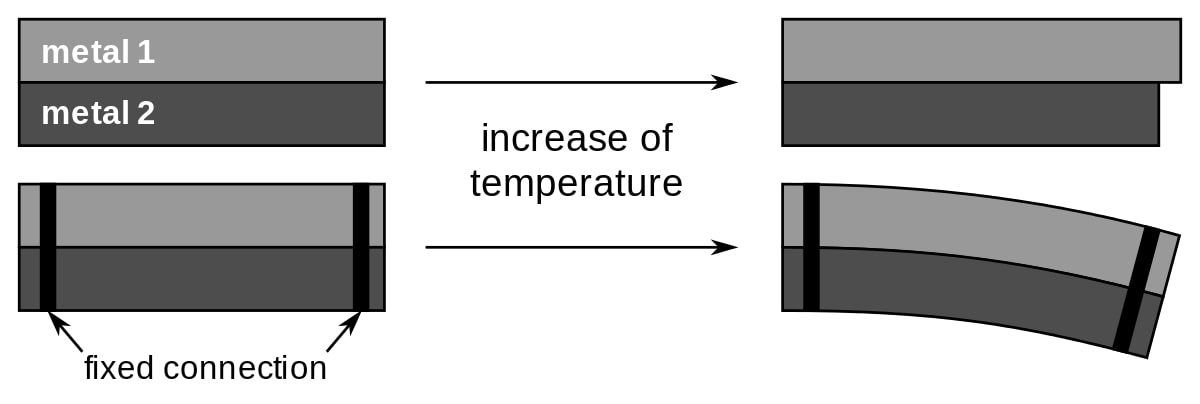
Bimetallic strip bending.
What are the advantages of using DC circuit breakers?
DC circuit breakers offer numerous advantages, including:
- After tripping due to a fault, a DC circuit breaker can be manually reset instead of being replaced, unless a large short-circuit current has been interrupted, in which case repair may be necessary.
- DC circuit breakers provide two protective functions:
- The long-time delay release with inverse-time characteristics.
- The instantaneous current release is used for overload and short-circuit protection, respectively.
- Beyond protection, many DC circuit breakers feature smart functions such as fault recording, communication interfaces, and electrical quantity measurement, enabling integrated monitoring and supervision of device and system distribution.
- DC circuit breakers are specifically designed to address arcing issues and include additional measures to quickly disperse electrical arcs during circuit opening and closing, thereby extending device lifespan.
There may be other advantages not listed here, but these are the most common and notable ones.
What are the common types of DC circuit breakers?
There are numerous types of DC circuit breakers, categorized into three main varieties: basic circuit breakers, ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), and arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs).
- Basic circuit breakers.
Basic circuit breakers come in four types: single-pole, double-pole, triple-pole, and four-pole circuit breakers.
- Single-pole DC circuit breakers.
Single-pole DC circuit breakers are designed to monitor the current in a single wire and trip in the event of a short circuit or electrical overload.
They are rated to distribute 120 volts to the circuit and handle currents between 15 and 30 amps.
Most modern homes are equipped with single-pole DC circuit breakers.
- Double-pole DC circuit breakers.
双极直流断路器设计用于同时监测两根导线中的电流流动。.
它们也被称为2极直流断路器、2P直流断路器、双极直流断路器、4极直流断路器、2P直流微型断路器或无极性直流断路器。.
您可以轻松识别它们,因为它们有两个并排的开关,连接在一个断路器内。.
如果两根导线中的任何一根过载或短路,它们会立即跳闸。.
双极直流断路器可为电路提供120/240伏或240伏的电压。.
它还可以承载15安培至200安培的电流。.
其中一些用于为需要大量电能的电器供电的电路,例如带烘干功能的洗衣机。.
- 三极直流断路器
三极直流断路器比单极直流断路器更实用。.
例如,如果一台机器内有三个需要保护的电机(具有相同的额定电流),使用一个三极直流断路器比使用三个单极直流断路器更实用。.
这将显著减少安装时间和空间需求。.
更重要的是,在负载故障的情况下,所有三个负载都将与电源断开,其中包括无故障负载,从而确保整台机器完全停机。.
- 四极直流断路器
四极直流断路器,类似于三极直流断路器的例子,如果您需要保护一台机器内的四个电机,这是一个更实用的选择。.
另一个例子是当您需要将备用发电机连接到开关设备时。.
因此,您可以采用四极直流断路器,而无需断开发电机的中性接地连接。.
您可以找到额定工作电压为1000伏、额定电流从65安培到25安培的产品。.
- 接地故障断路器(GFCI)
接地故障断路器专为保护线路对地故障而开发,特别是在接地元件与电流之间出现不安全电气路径时。.
住宅的某些电气规范要求安装此类断路器,特别是在容易潮湿的区域,如浴室、洗衣区和室外区域。.
- 电弧故障断路器(AFCI)
电弧故障断路器设计为在检测到电线内部产生电弧时跳闸。.
这种情况有时发生在损坏的电线或绝缘层变薄的电线上,这些情况可能引发严重的火灾隐患。.
基本断路器可能无法始终检测到电弧,因为它们仅在过热时跳闸。.
电弧故障断路器通常是新建住宅电气规范中强制要求的部分。.

双极直流断路器、AFCI和GFCI
15. 直流断路器采用哪些安装方式?
直流断路器的安装方式指的是它们如何在单个外壳或组件中使用。.
单位成本和更换的便利性是选择断路器安装方式时也应考虑的重要因素。.
安装方式也可能取决于断路器的类型或具体应用。.
直流断路器可采用以下任何一种常见安装方式进行安装:
- 固定安装方式
在这种安装方式中,直流断路器通过硬接线固定安装在框架上,或用螺栓固定在外壳或组件中。.
这被认为是购买成本最低的安装方式。.
它也是前部可安装且可靠的,适用于600伏及以下电压。.
当需要拆卸或更换直流断路器时,必须首先关闭电源。.
- 可拆卸安装方式
在这种安装方式中,直流断路器由两部分组成:底座和实际断路器。.
底座用螺栓固定并硬接线到框架上,而实际断路器则插入底座。.
采用这种方法,您可以更换直流断路器而无需重新布线,从而节省时间。.
这种方法购买成本适中,可前部安装,并具有良好的可靠性。.
它也适用于600伏及以下电压。.
更换直流断路器前,请确保首先关闭电源。.
- 抽出式安装方式
在抽出式安装方式中,直流断路器同样由两部分组成:底座和实际断路器。.
底座用螺栓固定并硬接线到框架上,而实际断路器则滑入底座。.
这样,可以在无需切断供给直流断路器的电源的情况下更换单元。.
您可以手动将直流断路器移入或移出,也可以使用摇进机构。.
尽管这种安装方式似乎更方便,但其购买成本最高。.
它非常可靠,可近端安装,并允许带电测试。.
此方法也适用于所有电压等级。.
为安全起见,拆卸或更换直流断路器时需要关闭电源。.
但此方法具有联锁功能,当您尝试拆卸单元时会自动切断电源。.
摇进机构可使直流断路器移动。.
通常通过棘轮或转动手柄操作。.
要将直流断路器从«连接»位置摇出,只需关闭单元的负载。.
内置联锁装置会执行此操作,因此直流断路器在开始摇出前会自动断开。.
抽出式安装方式无需为了检修一个直流断路器而关闭整个组件的所有电源。.
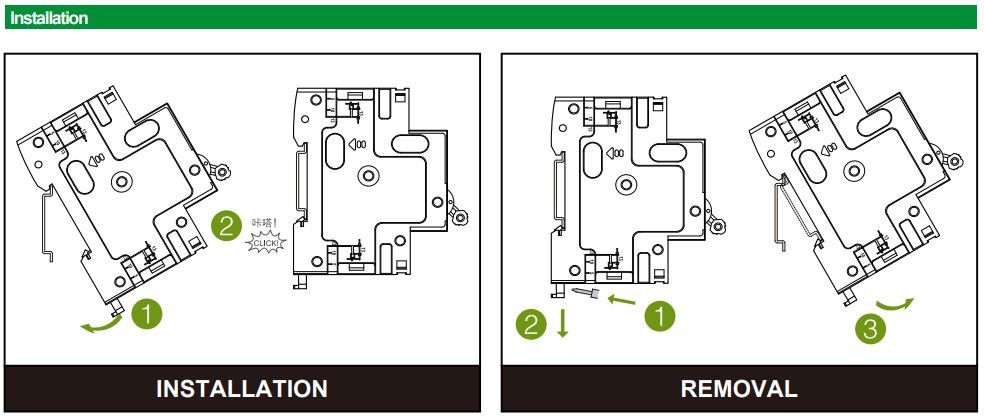
安装和拆卸示例
16. 直流断路器在LED灯上的用途是什么?
LED灯,如其缩写所示,使用发光二极管工作,而这些二极管只能在直流电下运行。.
这就是为什么常见整个电路使用直流电工作,但这通常仅在连接LED灯时如此。.
由于电路使用直流电,因此需要直流断路器进行保护。.
LED灯以高能效著称,可节省高达70%的能源,相比之下其他照明技术相形见绌。.
然而,LED灯有时价格偏高,且若提前损坏通常无法退款。.
正因如此,使用直流断路器对其进行保护至关重要。.
此处还需注意,LED灯可使用交流电和直流电。.
使用交流电的LED灯内置整流器,用于连接交流电路。.

采用LED照明的住宅
17. 直流断路器在太阳能电池板中起什么作用?
直流断路器通常安装在太阳能光伏(PV)系统中,用于保护部分组件。.
光伏太阳能电池板将太阳辐射转化为直流电。.
该直流电可用于为电器设备供电。.
太阳能光伏板以串联电路方式连接,根据其容量,一套装置可能包含多个电路。.
随后所有电路均接入光伏汇流箱,且每条电路均连接一个直流断路器。.
这确保了太阳能光伏板受到保护,因其被视为整个系统中最昂贵的部件——即使小型光伏装置的成本也可能高达数千美元。.
若太阳能光伏系统使用蓄电池组,该电池组也需连接直流断路器以获得保护。.
若太阳能光伏板产生的所有电能合并为单一直流输出,则同样需要连接直流断路器。.
另一需要直流断路器保护的部件是逆变器,其负责将直流电转换为交流电。.
最后,若设有直流负载专用配电盘,则必须配置一系列直流断路器。.
您可选择将太阳能电池板产生的电能用于交流电器设备,同时安装电力逆变器。.

住宅太阳能电池板安装
18. 直流断路器在电动汽车中的作用是什么?
电动汽车依靠大容量充电电池运行,而非依赖化石燃料。.
电池在专为电动汽车建造的充电站中进行充电。.
这些系统使用直流电工作,因此必须采用直流断路器。.
电动汽车是可再生能源技术的一部分,其环保设计为交通提供了可持续能源。.

电动汽车充电
19. 直流断路器在高精度工业焊接和设备中有何用途?
使用直流电的电弧焊机必须配备直流断路器保护。.
这是为了确保操作安全,并防止焊机受损。.
直流断路器也普遍用于直流电动机的保护。.
这类直流电动机具有广泛的工业应用。.
它们以易于掌握的控制、与自动化系统的集成以及瞬时响应时间而著称。.
因此,直流电动机非常适用于工业机床、自动化设备以及轨道和传送带等运输装置。.
此类机械的控制电路采用直流电工作,因而需用直流断路器进行保护。.
控制电路与电源电路因工作电压不同而相互隔离,但每条电路均由各自的直流断路器保护。.
额定电流和电压较低的是控制电路,因其仅用于处理控制信号。.

焊接行业金属加工
20. 适用于直流断路器的标准规范有哪些?
电气标准规范旨在保障从事住宅或任何其他场所电气安装或维护工作的人员、区域内的使用者以及财产本身的安全。.
其他规范按国家、州或地方分类,均具有类似的安全目的。.
此外,这些规范有助于建筑业主和城市通过遵守这套法律与指南来避免法律纠纷。.
- IEC 60364(建筑物电气装置)
IEC 60364是国际电工委员会(IEC)制定的建筑物电气装置国际标准。.
英国的BS 7671作为欧洲布线规范,遵循IEC 60364的框架,并补充了适应本国历史惯例的表述,便于电工和检查人员简化现场应用并实现合规目的。.
IEC 60364提供了电气系统安装与检查的标准规则。.
其他国家标准和指南参考IEC 60364以实现共同目标。.
- BS 7671(英国电气规范)
这是英国国家标准,即英国标准7671。.
亦称为《电气安装要求》和IET布线规范。.
该英国国家标准不仅提供电气安装标准,还涵盖电气安全布线及特殊装置和场所的标准。.
BS 7671详细规定了标称电压最高可达或包含1500伏直流或交流的电路。.
因此,该标准也详述了特低电压(ELV)范围(0至125伏直流和0至50伏交流)以及低电压(LV)范围(125至1500伏直流和50至1000伏交流)。.
该标准还包含欧洲电工标准化委员会技术实质协议。.
- CSA C22(加拿大电气规范)
CSA C22是加拿大标准协会制定的标准,涵盖加拿大境内电气设备的安装和维护。.
该标准规范是全加拿大布线指南的基础。.
此规范由来自同一行业及不同政府层级的大量志愿者共同制定。.
它规定了布线方法,提供了可接受的规范性模型。.
但也可采用其他布线方法,前提是必须首先获得当地执行该标准规范的管理机构批准。.
然而,该规范不适用于车辆、通信公用系统、铁路系统、船舶和飞机,因为这些装置拥有自身的标准规范。.
- NFPA 70(美国国家电气规范)
NFPA 70详细规定了美国的布线及设备安全安装要求。.
这是一项可在地方层面调整的标准,隶属于美国国家消防协会(NFPA)。.
虽称为国家规范,但它并非法律,而是通常被采纳为强制执行安全电气实践的标准。.
它也可根据地方管理机构投票制定的区域法规进行修订、更改或否决。.
请勿与NESC混淆,后者适用于架空和地下线路以及变电站的通信公用系统和电力系统。.
- UL489 and UL1077
UL 489 is the standard for molded case circuit breakers, while UL 1077 is for supplementary protectors used in electrical equipment.
According to UL standards (Underwriters Laboratories), most circuit protection devices should be inspected and covered by their recognition or listing services.
UL tests the devices, typically 2 to 4 times per year, to ensure that the materials and design of the originally recognized device remain consistent.
If the device has optional features, such as auxiliary contacts, UL will require additional testing.
Other standard codes may currently be implemented in your area.
It is best to consult the local governing authority or a licensed electrician to ensure your chosen DC circuit breaker complies with minimum safety standards.

International standard code logos
21. Can you replace or install a DC circuit breaker yourself?
Unfortunately, the answer is no.
When working with electrical components such as DC circuit breakers, precautionary measures must always be considered, and it is not a task for just anyone.
This is because installing or replacing a DC circuit breaker is a job for a licensed electrician and may even require a permit, depending on your location.
Electricians are required to take proper precautionary measures and adhere to electrical codes.
Failure to do so can result in fires, electrocution, or even death.
Electricians are also trained to determine the type of circuit breakers required for your home.
Typically, DC circuit breakers are mounted in fuse boxes, and a rail specially designed for their installation is provided.
DC circuit breakers protect individual direct current loads or main circuits such as solar PV arrays, inverters, or battery banks.

Solar battery banks
22. How to find DC circuit breakers in China?
You can shop for DC circuit breakers online on your preferred manufacturer’s website, on online marketplaces, or by using search engines and entering keywords such as “DC circuit breaker.”.
Generally, manufacturers have a product listing page where you can add your chosen DC circuit breaker to the cart, select the quantity, and enter payment details to complete the purchase.
However, to receive personalized service, you may first send an inquiry.
For example, if you choose Langir as your DC circuit breaker supplier, simply fill out the free inquiry form and include your contact details.
A sales professional will contact you using the provided details and assist with your order.
Langir accepts both small and large orders, as well as urgent orders.
For small packages, they typically use express delivery services such as FedEx, DHL, UPS, TNT, or EMS, which offer door-to-door delivery.
For large packages, they usually ship by sea or air.
Upon order confirmation, inspected DC circuit breaker stock will be shipped immediately, and you may receive your order within 2 to 3 days.

Langir product storage facility ready for dispatch











