Introduction
You may know about circuit breakers, but you may not know how to properly select the right one. An incorrect choice may cause equipment damage or even fire. This guide will tell you in detail the points and steps to pay attention to when choosing a circuit breaker, helping you to choose the right circuit breaker.
What Is A Circuit Breaker
A circuit breaker is an automatic protection device. It cuts off the circuit to prevent overloading or short-circuiting when the current limit is exceeded and can be reused.
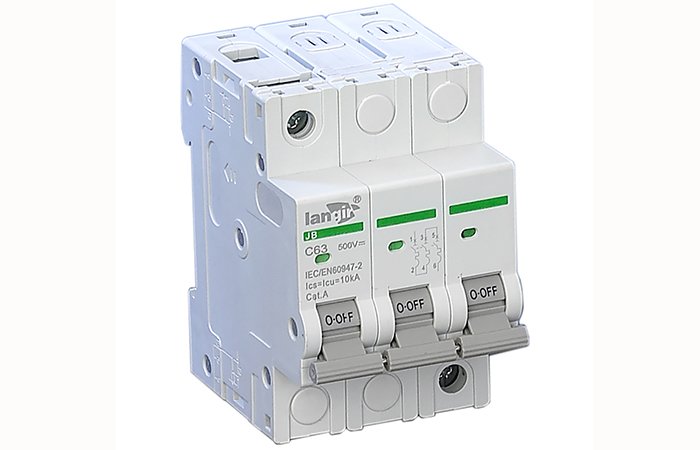

Working Principle of Circuit Breaker
When the circuit is overloaded, the metal blades inside the circuit breaker become hot due to the increased current. The metal expands or contracts with the temperature change. So the metal blades will deform due to heat and thus cut off the circuit. When the circuit is shorted, the coil inside the circuit breaker becomes more magnetic. The contacts are moved causing the circuit breaker to be closed.
Types of Circuit Breakers
Depending on the application environment, the type of circuit breaker needed will vary. Circuit breakers can be mainly divided into the following types:
MCB: Miniature circuit breakers are the most widely used circuit breakers. The rated current is small and is generally used in residential and small commercial applications.
MCCB: The shell of the molded case circuit breaker is made of plastic. It has a higher rated current and is usually used in industrial and commercial applications.
ACB: Air Circuit Breaker is also called universal circuit breaker. This type of circuit breaker is large and has a very high rated current. It is usually used in distribution rooms to protect the main power supply of large equipment.
AFCI: An arc fault circuit interrupter is usually installed in sockets. Fires can be avoided with this kind of circuit breaker.
GFCI: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter can protect the circuit. When the circuit current is detected to exceed 5 milliamps, it will cut off the circuit to avoid electric shock.

5 Factors to Consider When Choosing
When choosing a circuit breaker, it’s important to consider several factors to help you make the best choice for your needs.
Rated Current And Voltage
This is a crucial factor that is easy to verify. You can check the rated voltage and current by examining the label on the circuit breaker. Make sure the rated voltage and current of the circuit breaker are higher than the maximum voltage and current that the circuit can withstand so that the circuit can operate safely and stably.
Number of Poles
You also need to determine the number of poles of the circuit breaker. This depends on the number of phases and the voltage of the circuit. For example, if the voltage of the circuit is 120 volts, then you can choose a 1P circuit breaker.
Breaking Capacity
The breaking capacity of the circuit breaker is also a very important factor. When choosing, you need to make sure that the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker is higher than the short-circuit current value. This can effectively avoid equipment damage and personal injury.
Installation Space
Before choosing a circuit breaker, you need to use a tool to measure the dimensions of the installation space. This is done because circuit breakers are available in different sizes to ensure that the selected circuit breaker will fit perfectly.
Safety And Compliance
Safety comes first. Remember not to buy cheap circuit breakers without safety guarantees to save money. This may lead to greater disasters.

How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker
After reading this, I believe you already have a preliminary understanding of circuit breakers. Next, I will teach you how to select the right circuit breaker.
Step 1: Determine the load type
There are three types of loads: resistive loads, inductive loads, and capacitive loads. Choosing the appropriate circuit breaker will be made easier if you know the features of each load.
Step 2: Calculate the current rating
The circuit’s overall current rating must be determined first. A circuit breaker’s rated current needs to be somewhat higher than the total amperes. You can prevent short circuits by doing this.
Step 3: Select the type of disconnect curve
Common tripping curve types are B, C and D. You can confirm the type of circuit breaker based on the device. For example, table lamps are suitable for B curve; transformers use C curve; D curve is suitable for motors.
Step 4: Adapt to the Application Environment
When choosing a circuit breaker, you must consider the application environment. If it is used outdoors, you need to choose a circuit breaker with IP65 or IP67 shell. If the environment is humid, then you need to use GFCI.

Mistakes to Avoid
There are a few common mistakes you need to be aware of when picking a circuit breaker.
Mixing brands: mixing different brands of circuit breakers will lead to incompatibility. This can cause trips or even a fire
Ignoring the application environment: using regular circuit breakers in humid environments can result in the circuit breaker failure.
Using overloaded circuit breakers: the rated current is not higher the better. Using overloaded circuit breakers can cause wires to overheat.
FAQs
1. How often should circuit breakers be inspected and tested?
I recommend that you inspect them once a year. If they are faulty, repair or replace them promptly.
2. How long do circuit breakers last?
Usually, their lifespan is around 30 to 40 years.
3. Can I change the circuit breaker by myself?
If you are familiar with the electrical system, you can replace the circuit breaker by yourself. However, if you face more complex circuit problems, it is recommended that you contact a licensed electrician.
4. What is the difference between GFCI and AFCI circuit breakers?
GFCIs can prevent people from electric shock and are usually used in wet areas such as bathrooms. AFCI is mainly used to prevent fires and is required to be installed in living areas such as bedrooms.

