Do you get confused because your home is constantly tripping circuit breakers? Don’t worry, it’s usually caused by a faulty breaker. A circuit breaker is an important protective device for your home’s electrical system. When the current is overloaded or short-circuited, it automatically cuts off the power supply to protect the equipment. Over time, their performance may degrade. That’s why replacing circuit breakers regularly is a necessary step to ensure safety. This guide will show you in detail how to diagnose and replace a faulty circuit breaker.
Signs of a Bad Circuit Breaker
If your home’s circuit breaker shows any of the following signs, it may be failing:
Frequent tripping: The circuit breaker frequently trips for no obvious reason.
No current: The circuit will not be energized even if the breaker is started
Burning odor: the breaker feels hot to the touch and smells mushy
Physical damage: the breaker is cracked, discolored, or components are melted.
Age: If the circuit breaker has been in use for more than 15 years, the material may deteriorate and cause a failure.

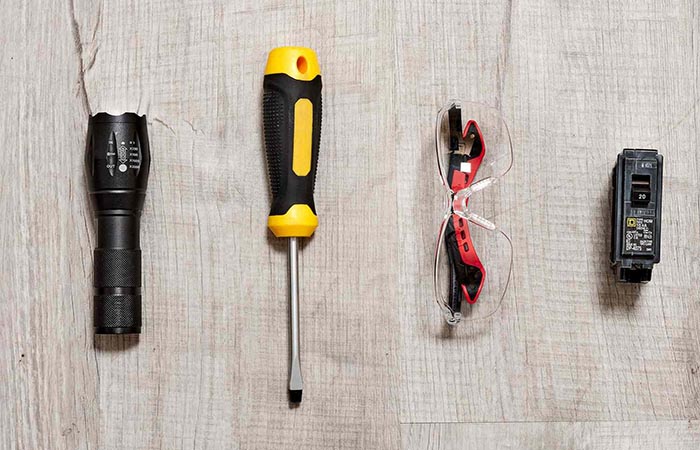
Tools You’ll Need
Before replacing the circuit breaker, we need to prepare some tools that will be used.
Voltage tester: Confirms whether circuits are de-energized.
Screwdrivers: Use insulated flathead and Phillips screwdrivers to prevent electric shock.
Needle-nose pliers: Used to hold and operate wires.
Safety gear: Wear insulated gloves and goggles during operation to ensure safety.
New circuit breaker: Ensure the brand, specifications, and amperage rating match the old breaker. Mixing brands of circuit breakers may result in incompatibility, which may be dangerous.

How to Replace A Circuit Breaker
If you want to replace a damaged circuit breaker yourself, you can follow the steps below:
Step 1: Turn off the power
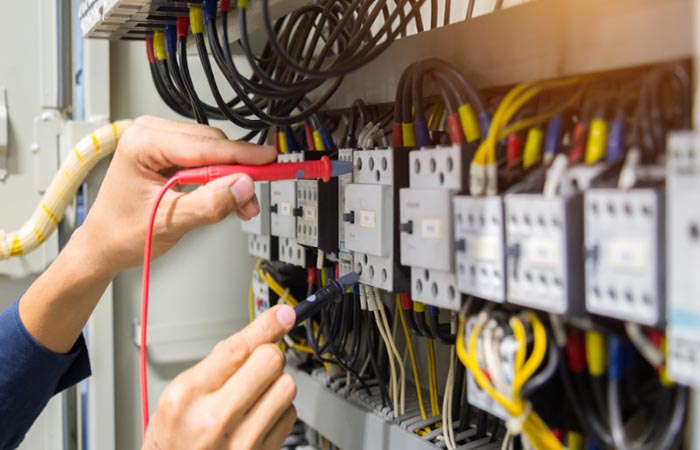
Locate the main circuit breaker and turn it to the “OFF” position. Use a voltage tester to confirm that the busbar does not have power.
Step 2: Detach the cover of the switchboard
Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove the cover screws. Store screws safely and check for rust inside the panel.
Step 3: Locate the faulty circuit breaker
Use an infrared thermometer or multimeter to locate the faulty breaker. Check for burn marks or loose connections.
Step 4: Remove the old circuit breaker
Grip the edges of the breaker and pull it out. If stuck, gently pry it loose with a screwdriver. Loosen the terminal screws to disconnect the wires.
Step 5: Install the new circuit breaker
Line up the new breaker with the bus bar and plug it in. Reconnect wires to terminals and tighten screws
Step 6: Turn on the power and test
Install the panel cover back on and restore main power. After starting the new circuit breaker, you can use a lamp to test the circuit for proper operation. If the light comes on properly, congratulations, the replacement was a great success.
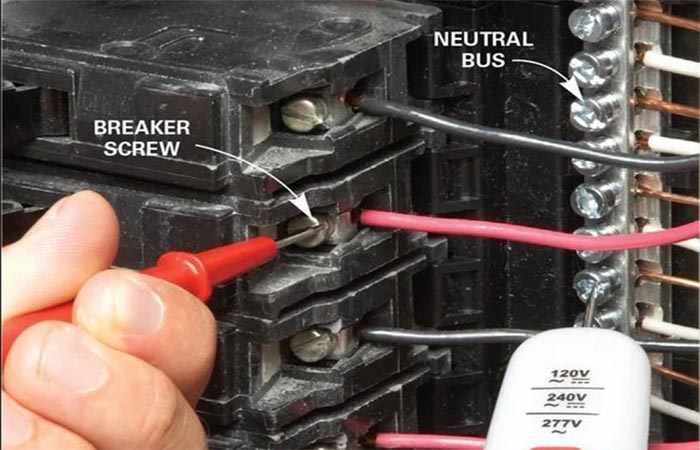
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Replacing a breaker seems simple, but ignoring key details can lead to serious risks:
Mixing brands: Using different brands can cause poor busbar contact, increased resistance, overheating, or even fire.
Over-tightening screws: Tightening the screws too much may increase the resistance and damage the wires.
Ignoring damaged wires: Failing to replace frayed or exposed wires invites future problems.
Skipping safety gear: Always wear insulated gloves and goggles to avoid electric shock.
Incorrect breaker type: Avoid using standard breakers in damp areas like kitchens or bathrooms. You should use special circuit breakers such as GFCI/AFCI types.
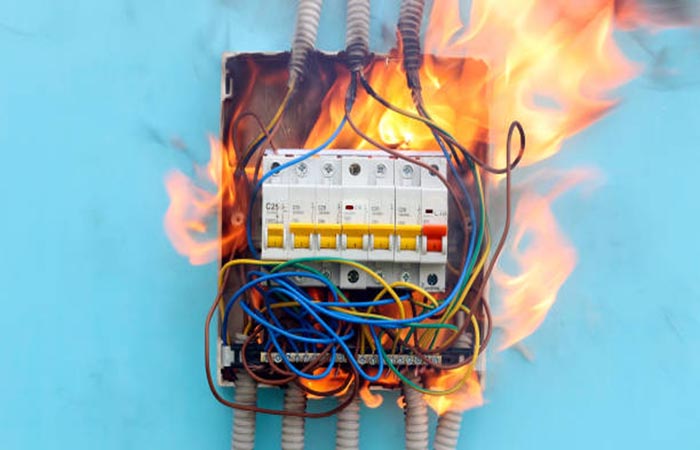
When to Call an Electrician
If you notice any of the following, immediately shut off the power and contact a professional electrician:
- Smell a pungent burning odor
- Sparks or flashes of light inside the switchboard
- Ageing of the switchboard
- Damaged wires such as cracked insulation or exposed metal wires.
Aluminum wires require special connectors to effectively reduce the risk of fire. Electrical issues may seem minor, but hidden dangers can escalate into disasters. Therefore, never choose to make repairs on your own just to save money. The risk can be increased if proper care is not taken. The right thing is to hire a licensed electrician. Make sure your home meets safety standards to protect you and your family.

Maintenance Tips for Circuit Breakers
I will share some maintenance tips. You can extend the life of your home’s circuit breakers effectively when you master them.
Regular testing: Use the “TEST” button on GFCI/AFCI breakers for self-checks.
Cleaning: Excessive dust may cause a fire. Therefore, regularly wipe the panel with a dry cloth to keep it clean.
Labeling: Tag each breaker in the electrical panel for easier troubleshooting.
Replace old breakers: Proactively replace units older than 15 years.
FAQS
1.Can I install a higher-amp breaker to stop tripping?
No! This can overheat wires and cause fires.
2.Is it normal for a new breaker to feel warm?
Slight warmth is normal. If it feels hot, unplug devices—it may be overloaded.
3.How long does the replacement take?
Professionals need about 20 minutes. Beginners are advised to allow 1 hour.